Tip #780: What’s a Proxy File?
… for Codecs & Media
Tip #780: What’s a Proxy File?
Larry Jordan – LarryJordan.com
Proxy files are a tradeoff: faster performance with lower image quality.
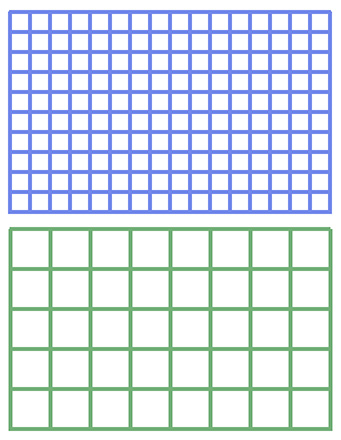

At its simplest, a proxy file is a “stand-in,” a proxy, for another file. However, when it comes to media, a proxy file is a smaller version of the original file.
This reduced size provides several benefits:
- Smaller storage requirements
- Slower bandwidth requirements
- Ability to run on older or slower systems
However, while smaller files are a good thing, the real challenge is to create proxy files that provide a similar geometry to the source file, otherwise, any effects you create with them will need to be altered when you switch back to the source media.
For this reason, proxy files, by intent, are 1/4 the size of the source image but with the same aspect ratio as the source file. This decreases file size and bandwidth by 75%, but matches the geometry of the source.
The easiest way to create this is to divide each frame into a series of 4-pixel grids, then remove 3 of the 4 pixels in each grid. This means that a 4K (3840 x 2160) becomes 960 x 540. Often, many proxy files use 1280 x 720 because this is already a common video format.
While not providing the same image quality as the source media, the image is good enough to use for editing, until the time comes for final effects, color grading and output.


Great
Need the reverse process detailed! Gotchas?
Best, as always,
Loren
Loren:
Which reverse process are you looking for?
Larry